Despite the short period of life lice, they cause a lot of trouble. Severe itching that accompanies the patient day and night causes discomfort. Lice never go hungry.
They constantly feed on blood, thanks to which their intensive reproduction takes place. Getting on a person, they multiply so quickly that their number after a week increases several times. It is necessary to study the life cycle of lice in order to know how many days after infection it is necessary to begin treating the disease.
Lice development cycle
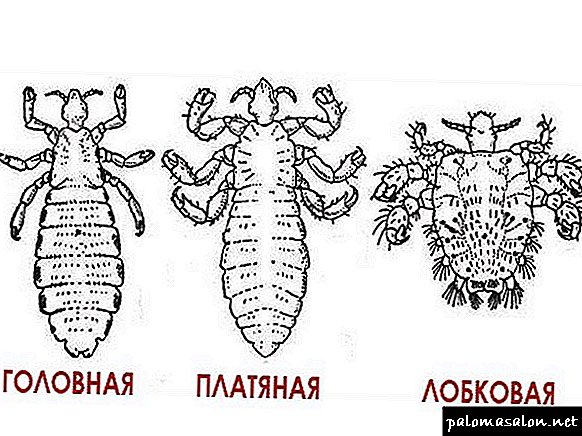
Everyone knows that there are three types of lice on the human body: head, clothes and pubic. Each of these species has its own specific features, however, in general, the reproduction and development of all types of lice are the same and differ only in small details.
It is no secret that the development and reproduction of head lice occurs very rapidly. So, already sixteen days after the egg was laid by a sexually mature female, the louse hatched and developed from it could itself lay eggs.
It is precisely in connection with such rapid developmental periods already a month after infection with head lice that an incredible amount of insects and nits can appear on the human head without appropriate treatment.
The full period of life expectancy for lice is 32-42 days. And during this time the head louse has time to lay from 80 to 140 eggs, the pubic louse lays about 50 eggs, the clothes louse can lay as much as 300 eggs.
As a rule, the whole life of a head louse occurs on the same human head, but there are cases of lice moving on the head of another person in case of close contact, as well as in some other situations, which leads to infection with lice.
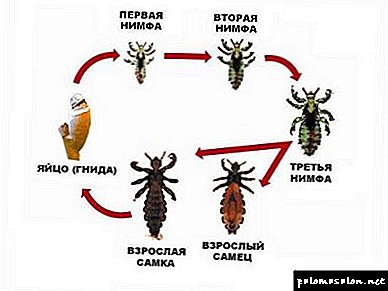
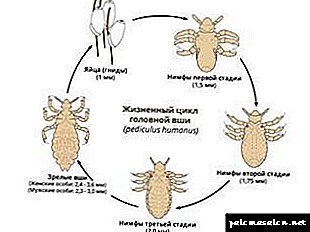
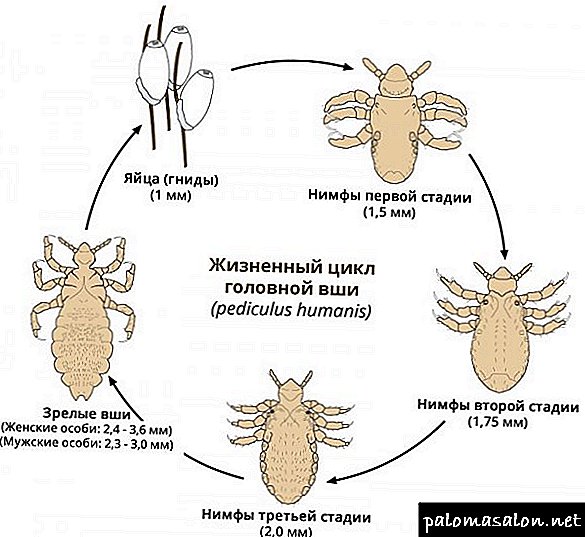
The whole cycle of development of lice can be noted as a nit - a larva - a nymph of the first age - a nymph of the second age - a nymph of the third age - adult louse After each molt the nymph from one age passes into another.
The need for molting is that during the growth of the soft tissues of a nymph, the growth of chitinous cover is absent and it must be periodically changed. The whole process of molting lasts around five minutes, and after forty-five minutes the new cover becomes more dense and the nymph can start feeding.
The larva, having turned into an adult female louse after the last molt, already during the first or second day begins to mate and lay eggs, attaching them near the root of the hairs. While still in the genital glands of the louse, the egg is smeared with a special sticky secret with which it then leaves the oviduct.
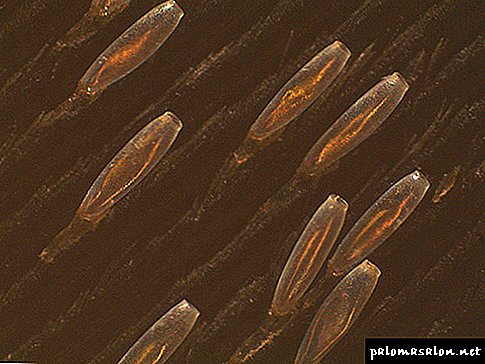
Nits have a very small size, which complicates their detection. In addition, they are often confused with dandruff due to the great similarity in color and shape. However, dandruff is easily removed from the hair, unlike nits.
The period of development of nits under suitable conditions for it is from 5 to 8 days, after which the larva of the first age appears from it. After only one or three days, such a larva turns into a nymph of the first age after it is first saturated with human blood and passes the first molt.
Moreover, the lack of food in insects such as lice is not due to their stay just at the source of their food. Due to this fact, as a rule, there are no delays in the development of head lice.
As for the larva, it differs from an adult individual only by its smaller size and weak development of the reproductive system. The optimal conditions for the development of nits and lice is considered to be the temperature in the region of 30-31 degrees Celsius, which usually corresponds to the temporal and occipital parts of the human head.
When the temperature differs from the specified interval, the development of nits slows down until it stops completely, which is typical for temperatures outside 22 and 45 degrees Celsius.
It is also worth noting a specific feature of the process of emergence of larvae from the egg. The fact is that the larva, even after it has pierced the shell of the egg with the help of the jaws, still cannot get out of it to the surface of the head.
In this regard, in order to get out of the eggs of the larvae, there is a very interesting way: they begin to breathe actively, so that the air passes through the entire digestive tract and goes out in the anus, then, having accumulated at the bottom of the shell, it simply pushes the larva out.
And it is very interesting that when a larva is born, it does not have any sexual signs and only later becomes a female or male, depending on which insects of which sex is not enough.
Thus, knowing the peculiarities of the development of lice from an egg to an adult, it is possible to predict the characteristics of the course of such a disease as lice, as well as the possibilities of its treatment.
Lice and nits: incubation period, treatment (re-treatment time)
From the moment of the first meeting with lice and until the first symptoms appear, it can take 30 days, sometimes more. Therefore, one can imagine how many lice already run on the skin, remembering where and when an infection could have occurred.
Personal hygiene of an already infected person does not affect the rate of reproduction of lice. The higher the temperature (from 30 degrees) and the greater the humidity, the faster the lice multiply.
In the absence of contact with the body in the environment at a temperature above 40 degrees and below 20 degrees, further development does not occur. Outside the body, head lice live no more than 2 days, and the body temperature always coincides with the insect's “comfort zone”.
Under the phrase "incubation period" we understand the time from the moment of infection to the first symptoms. There is still a biological understanding of this term. Then we are talking about the development of lice eggs, that is nits. This is the time interval for which the conversion of lice from nits.
How pediculosis caused by Pediculus humanus capitis lice is transmitted
Lice are insects that are "committed" only to humans. Therefore, you can only get from a patient with head lice. You should not listen to the legends that lice can live on pets for a while. They have their lice.
Lice do not know how to jump and fly. Therefore, infection is possible only with close contact at a small distance, when it is possible to crawl. As they say head to head. By the way, lice have excellent dexterity when crawling.
If we talk about nits, they are still. But they can get to a healthy person from the patient through hygiene items and personal items (comb, hat, towel, pillow, etc.)
How are pediculosis infected?
Places of infection may be different: school, kindergarten, camp, public transport, hotels, hospitals, hairdressers, trains and other popular places.
For infection, you need a suitable place (the options are listed above) and two people who have been in contact with each other for some time, one of whom has lice.
How can you get lice: you can only become infected through direct contact. Being in different corners of the same room with a sick pediculosis man, a healthy person will remain still healthy.
Children often award each other with head lice. Pubic pediculosis can be acquired with frequent changes in sexual partners and promiscuous sexual relationships.In children, pubic louse may settle on the head and eyelashes.
Pubic louse in children is usually a "criminal" sign - a symbol of the sexual use of the child. The clothes louse most often settled in the homeless.
How quickly do parasites multiply on the head?
In this issue there is nothing to console. Lice breed quickly enough, even rapidly. One louse per day lays an average of 5-10 eggs (nits), which, depending on the temperature and humidity, turn into ordinary lice in 3-4 weeks, which can also lay eggs.
How lice multiply on the head: as soon as the adult louse managed to move to the head untouched by its tribesmen, it does its best to provide the owner with a new population of lice, the louse feeds and lays eggs (nits) in a full form.
The life cycle of Pediculus humanus capitis lice
From its inception to the death of Pediculus capitis, there are 4 stages of development: egg (nits), larva, nymph, adult.
The egg from the oviduct is removed in a sticky lubricant, which forms the shell of the nits. Later, this lubricant in the form of a capsule hardens already on the hair, and firmly holds the nits in place. Capsule protects developing lice.
Very interesting is the release of the larvae from the egg. The shell of the nits is dense enough, and to overcome this shell, it must be pierced. This is what the lice larvae do, piercing one end of this cocoon with their jaws.
The louse's appetite is very good and they eat every 2-4 hours. In order to actively multiply they need strength. They do not have hunger strikes, as there is no problem of finding food. Food is always near. When the larva came out of the shell nits - this is a nymph.
The nymph molts two more times to turn into an imago - a mature individual. Shedding is necessary because the cocoon in which the larva lives does not grow. A nymph needs protection from adverse environmental factors and medical shampoos. As the larva grows, it needs to change the protective “clothes”.
Mature lice can begin to mate only after the first bite. After two days, the female lays eggs, then laying eggs occurs every day, a maximum of 10 pieces.
If you briefly describe the reproduction and development of lice in terms, it will look like this:
- the incubation period is from 16 days to 30 days,
- it takes a week to ripen the nits
- the larva develops 1-2 days,
- The nymph develops 5 days before the first molt (the nymph of the first age) and the nymph lasts until the second molt for 7-8 days (the nymph of the second age),
- adult insect (imago) begins to mate in 1-2 days after transformation from a nymph. Sexually mature louse lays eggs every day.
We can say that on average, it takes 20-21 days for a louse to come out of the nits.
Now, when you know how lice become infected, how lice reproduce on the head, how many nits the adult lays per day and after what time the young hatch from nits, it will be clear why the workout must be repeated several times. There are many medications aimed at inhibiting the activity of insects or their destruction.
All funds for lice can be divided into those that kill only living individuals, and those that also kill nits (pediculosis preparations - pediculocides with ovocidal activity).
Folk methods of combating pediculosis, there is no less. Read more about pharmaceutical preparations here, and about folk remedies against lice.
Most drugs are NOT EFFECTIVE against nits and therefore, it is necessary to re-treat the head. Means, destroying nits, in its composition contain the substance MALATHION.
In the presence of any chronic diseases, as well as in the treatment of children under two years of age, it is better to consult a physician for the proper selection of medication.
Now, when you know how lice get infected, how lice reproduce on the head, how many nits an adult lays per day, and after what time the young hatch from nits, it will be clear why the treatment should be repeated several times.
The interval of 7 days is necessary for fixing the effect. If after the first treatment some nits manage to survive, the larvae that have hatched in a week can “start” the process from the very beginning.
In order not to meet pediculosis without saying goodbye, a week after the first treatment procedure, it is necessary to repeat the “session” of treatment of the head with the chosen remedy.
Breeding lice. Sexual cycle lice
Lice are dioecious, but there are hermaphroditic individuals (Nuttall and Keilin) between the head and wound louses. In appearance, male lice are well distinguishable from females, primarily in their smaller size. The rear end of the male body is rounded, and the female is split.
The male genitals consist of two pairs of bag-shaped testicles, semiproducts, accessory glands, the family of the seven-channel and the copulatory organ with the parts serving it. The male's genital opening is shifted to the top and lies behind the anus.
The reproductive organs of the female are formed by two five-tubular ovaries, two short oviducts, an unpaired oviduct with a uterine sac, seminal receptacle, glue glands and a vagina.
Mating lasts 20-40-70 minutes. It can be performed at any time. The female is able to copulate immediately after the last molt, and the male only a few hours after it. Pairing wardrobe was valid for 15-20 days, head - for 7-12 days.
Fertilization in internal lice. Mature nits are squeezed out through the oviducts into an unpaired excretory sleeve, and, like a syringe piston, it pushes the secret of highly developed glue glands in front of itself.
Before laying the female body lice moves animatedly. When she chooses a suitable place, she wraps her hair around the hair or thread and stops. From the genital opening a drop of transparent secretion of glue glands protrudes, which covers the hair.
After a few seconds, the louse crawls forward, and the nit turns out to be already glued to the substrate. The process of laying eggs lasts about 17 seconds. Glue secret in a frozen state is very strong and resistant to various chemicals. Caustic reagents can soon destroy the very hair on which the nit sits, rather than dissolve its glue.
A well-fed female can lay eggs without fertilization, but nothing hatch from them. Not all eggs laid by the fertilized female give larvae. Of 1158 eggs kept at + 30 °, about 70% of the larvae (Nuttall) hatched, the rest of the eggs were either not fertilized, or the embryos died in them during their development.
Bacot observed the laying of 91-97% of fertilized eggs. Obviously, in this respect large variations are possible in some cases. The most important conditions for egg laying are: abundant food and temperature not lower than + 20 ° and not higher than + 37 °. The optimum for masonry is about + 32 °.
In one of the experiments, 65 female body lice at + 22 ° for two days laid only three eggs, of these females 35 were transferred to a thermostat at + 30 °, here the lice gave 188 nits a day. A body louse puts 6–11–14 nits a day, and in her entire life — no more than 295. A head louse gives no more than 4 per day, and in a lifetime, no more than 141 nits.
Nits of various human lice are somewhat different from each other. The isolation of ploshchits in this respect is undoubted: their nits are pear-shaped, 0.65–0.67 mm long, with a high dome-shaped lid. Body and head lice in the extreme forms of nits also differ from each other.
The head louse egg is oval with a slightly convex and moderately high lid; its length is 0.75–0.8 mm; it is glued to one hair, and not to cross them.
However, these signs, apparently, do not in all cases allow us to accurately distinguish between nits of head and body lice, since, due to variability, their extreme variants find each other. The question needs further study.
Conditions for breeding lice. General biological data
At temperatures below + 22 ° C and above 40-45 °, there are no larvae hatching from Rnid (Nuttall). Alternating cooling slows the development of lice. In a periodically removed and put on dress development is delayed up to 6 weeks. Optimum development of 30—31 °.
In non-removable clothing, the larvae come out of the nits in 7-10 days. In short, 4 days of fetal lice development cannot be (Nuttall).
From consideration of these data, we are convinced of the retarding effect of dryness on the development of lice. From nits of head lice at + 32-35 ° the largest number of larvae goes on the 7th day, yet the development lasts from 5 to 9 days.
Nits withstand without harm for themselves a 10-minute immersion in kerosene, gasoline and ether, a 2.5% solution of carbolic acid kills them in 10 minutes, 2% Lysol — in 5 minutes, sublimate vinegar and glycerin — in 1-2 minutes .
The procedure of shedding the skin lasts about 5 minutes, after 3/4 hours the young skin becomes denser and the louse can already suck blood.
General biological data
The full life cycle of lice of the genus Pediculus is composed of the following periods:
- embryonic development under the cover of nits - from 4 days to 6 weeks,
- postembryonic development
- mature phase.
The life cycle of a body louse — from the moment of laying eggs to the beginning of laying the female that came out of this egg (from egg to egg) —when it is kept on the human body lasts 16 days (Hamer).
In general, a clothes louse can live up to 2 months, the usual rate of the duration of its life cycle, not counting embryonic development, is 5 weeks, while the head louse lives for about 4 weeks. By the end of her life, a female with head lice can have 4,160 descendants (children, grandchildren, great-grandchildren, etc.).
The ratio of lice to temperature is characterized by the following data: A 30-minute stay of lice in dry air at 49 ° does not kill them, at 54 kills in 35 minutes. Air and water at 55 ° kill them in half an hour, the temperature in —12s does not immediately kill the lice, which, first of all, numb.
More about lice
Few people know that lice do not jump. In addition, they do not know how to fly, so lice are transmitted from person to person, either through personal and close enough contact, or through general use of clothing, home textiles and personal hygiene items.
If you want to protect yourself from possible infection with head lice, protect yourself from unchecked contacts with people. But remember: lice are not always transmitted to another person through direct contact with infected skin.
If you are on public transport or in another place where there are many people at the same time next to each other, you will notice a suspiciously itchy person, move away from him.
When visiting pools, wear a bathing cap made of rubber over the curls. As mentioned earlier, the lice do not jump, but they float perfectly.
Therefore, the risk of infection with head lice while swimming in the pool or in a closed pond is quite large. Do not allow anyone to use your comb and towel.
Lice reproduce fairly quickly - the developmental cycle from the larva stage to the adult stage is eight days. Reproduce offspring they are capable of the twentieth day of their lives.
The lice population feeds on human blood. To get to the blood, lice bite through the skin and leave small, but noticeable microraniums on it. The first symptoms of the onset of the disease are severe itching on the temples, the back of the head and on the skin behind the auricles.
If lice are not destroyed within a few days after their appearance, lice begin to actively multiply, covering new areas of the head with their larvae. Lice have an elongated elongated body, which is equipped with short, but tenacious legs, allowing them to quickly move through the skin and hair.
When hungry, lice are silver or amber in color. The body of a well-fed louse is colored in blood. The temperature they need for life is thirty-six degrees Celsius and above, and lice die at temperatures of twenty degrees and below.
Thus, the temperature of the skin of a person is ideal for their life. Once outside of human skin, lice die quickly.
The lice development cycle implies their external change.Lice larvae have a small size that allows them to merge with the hair shafts.
An adult head louse lays eggs, called nits, by attaching them to the hair roots using a special sticky substance that its digestive system produces. This natural glue cannot be dissolved with water, therefore it is pointless to fight against the appearance of lice and nits with the help of ordinary shampoos.
After a while, small nymphs hatch from nits, which by their appearance repeat the appearance of adult lice, but differ significantly in size.
In a state of larvae, lice individuals live for at least several days, during which the lice grow, receiving energy for development from human blood. On the tenth or twelfth day, a fertile period begins in lice, during which lice multiply, laying eggs of nits.
The life cycle of lice is thirty days, but during this short time the lice have time to reproduce offspring several times, the total number of which can reach up to three hundred nits.
Manifestation of the disease
Once you know the details about the cycle of development of nits, as well as about how many adult lice live, read about the signs of louse skin damage.
Please note that self-diagnosis does not always lead to confirmation of the presence of this disease.
Human skin has a huge number of nerve endings that can provoke itching, reacting to external or internal stimuli.
The first signs of the appearance of lice, especially when they are in the nits stage, often coincide with the usual itching of the skin caused by a nervous breakdown of varying strength.
Many people do not know how long it may take before the head lice finally take over the rights of the new owners of hair. On average, this period is equal to seven days, during which the louse will set aside nits, and those will have time to hatch and begin a new stage of their development.
But when the offspring of the parasite is born, it will be impossible to ignore the discomfort of their countless bites.
Doctors-dermatologists have an unwritten rule that says: if a sick person contacts with other family members or shares one room with colleagues, you need to be treated not only for the sick, but also for his environment.
Infection may not occur, but you should exclude any possibility of lice on other people's heads.
It will become a food for the parasites and an incubator that supports the desired temperature environment, outside of which lice do not live.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of pediculosis can be as follows:
- severe itching on the skin
- microblocks and small swollen, acne-like tubercles on the skin,
- barely noticeable eggs, covering in abundance the hair roots.
These symptoms are quite average. People have a different pain threshold.
Some of them immediately find that they have lice on their heads, while others do not perceive their bites for a long time. If you ignore the disease for a long time, you can put in the blood of a purulent infection called pyoderma.
In addition to medical drugs, from nits and lice can be eliminated with the help of folk remedies.
Pediculosis treatment
Do not ask questions about what appear lice, if they have already settled on your head.
As soon as you find them, immediately visit a doctor or start treatment at home. There are several effective drugs that can help you get rid of this problem.
Drugs that fight against the manifestations of the disease:
- 1% solution of malathion,
- boric ointment
- 20% solution of benzyl benzoate,
- "Pair plus"
- "Phenotrin".
An effective and inexpensive means to combat head lice is Medifox, which you can see the photo below.
Photos of other tools and instructions for their use you can find on various forums. Do not forget to care for the scalp after treatment.
Radical preparation for treatment is shaving the hair in the affected area, to which not everyone agrees.
If there are no curls on the head, the lice will have nothing to attach to their eggs and no place to hide. Lice rarely live on exposed skin outside the hair, so shaving is still an effective way to control lice.
Unfortunately, this method is not suitable for everyone - many women, even when faced with pediculosis, are afraid of losing their hair. To remove most of the nits and lice from the hair, without shaving them, you need to put on curls the drugs that kill the lice and dissolve the composition by which the eggs are laid on the hair.
After you apply the treatment composition to the curls, roll your head into the polyethylene. This is an important rule that will allow the drug to work more efficiently.
After combing lice and nits need to take a shower and wash the treatment solution from the head. How many procedures you need to completely get rid of nits, you can only determine by experience. Lice need to fight until signs of their presence disappear.
If you want to deal with lice at home, remember that lice are afraid of kerosene, vinegar or chemerichnoy tincture.
After applying these tools you need to carefully care for the scalp. Such compounds have a strong effect not only on lice and nits, but also on the epidermis, which needs careful restoration.
Care for the scalp, which has suffered lice, you need with the help of pharmacy tools, oils or home decoctions, as well as other self-made drugs.
Pediculosis is not a sentence. You can get rid of parasites in a fairly short time. The main thing - do not run the problem and do not give lice to multiply.
How quickly do lice grow on the head?
Some still mistakenly believe that head lice, that is, reproduction of lice on the head, can affect only people who seriously neglect the rules of personal hygiene. In fact, such a situation can occur with anyone, and this will not affect the age or gender of a person, nor his social position or commitment to cleanliness.
It is not easy to deal with such a problem, as the parasites die hard, develop rapidly and postpone their offspring. However, if you understand the development cycle of these insects, then the issue will be a little easier to solve.
Reproduction of lice occurs very quickly. Starting from the time of egg deposition and until the day when an already grown individual postpones its own offspring, it takes just over two weeks. However, such terms are respected in the event that the parasites are not affected by any negative conditions, such as temperature changes.
In case something prevented lice from growing and multiplying normally, the period from egg to egg can be a whole month. As a rule, after thirty days a huge number of parasites are already on their heads, and a little later their presence becomes intolerable. All the symptoms of pediculosis, which are almost impossible to tolerate.
It is interesting. The rate of lice development does not differ in representatives of different types and forms. Different types of differences are observed only in some small details.
Of all the existing types of lice on the human body, only two species can live - head and ward. The second, in addition to the skin itself, live on the patient's things, often leading to re-infection. However, regardless of the place inhabited, the life cycle will not have fundamental differences.
Appearance of nits
Lice are among the insects that undergo incomplete transformation. This type implies the absence of a full-fledged stage of a typical larva. For most other insects, this period implies the formation of an organism that looks and feeds completely differently.
In the life cycle of adult lice, the so-called larval molting period is distinguished.After a couple of days after the last one, the female begins to mate with partners. Only a few hours from the moment of fertilization is enough for the female to start laying eggs.
Unlike most other insects, head lice do not face the problem of hunger. Their feed, human blood, is always within walking distance.
Lice do not tolerate hunger. Each individual must eat at least once every four to five hours. Without feed, they die in a few days.
Lay eggs are placed on the hair, and the distance from them to the roots may be different. Future offspring are kept in this position due to a special sticky cap. The resulting egg in the shell is called "nits."
If you examine it under a microscope, you can see a kind of bag that fits tightly on the hair. From the side it will be possible to notice only a small dash of white color.
The further course of the life cycle
The next stage of the developmental cycle is called the larva of the first age. Externally, it is not much different from mature individuals, the main difference is in size.
Further life cycle of small lice is as follows:
- As soon as the parasite reaches the skin and eats for the first time, the process of larval molting will begin.
- As a result of the first saturation, the louse will enter the nymph stage.
These stages are repeated two more times. Thus, lice survive three larval molts and three stages of the nymph.
Upon completion of the third molt, the insect becomes a full-fledged adult, capable of laying eggs.
Details of the development process
Nits are unable to immediately leave their eggs. With the help of her jaws, she does pierce the lid, but she will not be able to get out this way. In order to leave the shell, the nit begins to breathe actively. The resulting air exits through the insect's anus, accumulating at the bottom of the egg. When it is typed enough, it simply pushes the nits out.
How quickly head lice can reproduce:
- Nit is formed in 5-8 days.
- After hatching, the larva becomes a nymph in 2-3 days, and sometimes even a day.
- Before the transition to the nymph of the second age passes 5 days.
- The nymph of the third age appears after another 8 days.
After this, the louse becomes a full-fledged adult. It usually dies in about a month, but the longest recorded life of a matured louse is 46 days. Mating with males occurs already in the very first hours from the moment of transition from the nymph stage to the adult one.
Breeding features
Females do not require multiple matings in order to fertilize all available eggs. This happens at a time, but the eggs are laid gradually. Every day, the female will produce a small amount of offspring, which varies depending on the type of insect.
The number of eggs per day for lice:
- Clothes - up to 10 pieces.
- Pubic - up to 3.
- Head - from 2 to 4 eggs.
Thus, for all the time of its existence, the pubic louse lays about 50 eggs, the head one - up to 140, although most often the figure does not exceed 80. Most of the offspring produce a wardrobe look, which in time manages to create about 300 eggs.
The shell, through which the nits are attached to the hair, is formed in the process of gestation, inside the female. In its sex glands is a sticky secret that accumulates on the future eggs.
Some of this secret leaves the body even before procreation is postponed, but most of it remains on the nits. The substance gradually hardens, firmly attaching the future louse to the hair.
What conditions are required for reproduction?
Lice and their reproduction largely depend on environmental conditions. The development of nits requires a certain temperature:
- The best indicator is 30 degrees.
- If the temperature falls below 20-22 degrees, the nit will stop developing.
- The same thing happens if the thermometer shows more than 45 degrees.
If the temperature around 30-31 degrees is maintained around, the reproduction of lice will pass easily and quickly. However, this is influenced by several factors. For example, it is easier for adults to mate, if you do not need to spend time searching for each other. Thus, the more lice on the head, the faster they multiply.
If several people infected with lice live in the same room, the individuals will have an even greater choice of partners. It is for this reason that insect parasites caused so much trouble in the barracks during wartime.
Most often, lice are poisoned with shampoos containing insecticides. However, the most effective method of struggle is still shaving followed by water procedures. If the parasite cannot lay its larvae on the hair, it will simply be washed off over time. Prophylactic measures to avoid lice, does not exist.
The speed and features of breeding lice
As soon as lice get on the scalp of a person, they immediately begin to feed on blood. It is the blood that allows the female to lay eggs. Without human blood, an adult does not reproduce and dies from hunger in 3-4 days.
Penetrating into the scalp, it releases a special substance so that the blood does not coagulate and it is convenient to eat. This substance causes severe itching in the patient.
As soon as the female fed, after 1-2 hours she begins to lay eggs. Lice breed very quickly, as the male does not have to search for a female for a long time. Also for parasites, human skin is an ideal place to live and reproduce.
To quickly develop they need a temperature of 22 to 45 degrees. Since the normal temperature of a person is 36.6, the life cycle of parasites proceeds very quickly.
 As soon as the time of hatching nits comes, the insect pierces the cocoon of the larva with the help of jaws. In this case, the nit itself is not able to get out of the egg itself. But she begins to actively breathe, pushing air through the digestive system into the anus.
As soon as the time of hatching nits comes, the insect pierces the cocoon of the larva with the help of jaws. In this case, the nit itself is not able to get out of the egg itself. But she begins to actively breathe, pushing air through the digestive system into the anus.
The accumulated air pushes the nits out of its cap. A nymph appears, which immediately starts feeding on blood.
There are several stages of development of parasites:
- the development of nits occurs about a week.
- Under favorable conditions, the larva turns into a nymph in a day. If conditions are not very favorable, it takes 3 days to turn into a nymph.
- Next, the nymph goes through another 2 development cycles. After 5 days, she matures and changes its cover.
- After 8 days the nymph sheds again and the third stage of maturation begins.
- As soon as the nymph turns into an adult, she begins to lay eggs.
It is necessary to start treatment at the initial stage of development of pediculosis to prevent the reproduction of parasites.
When do they start laying eggs?
If the conditions for life of lice are stable, its life on the scalp will be more than 1.5 months. As soon as the nymph finishes its development, she has already mated with the male for an hour.
Fertilization occurs immediately, and the female is able to lay eggs the next day. An adult individual lays 4 eggs every day. But since there are a lot of females on their hair, a huge number of eggs are laid per day. For the entire cycle, the female lays up to 140 eggs.
Passing through the sex glands of an adult insect, the egg is smeared with a special secret, due to which the nit is firmly fixed on the hairs. When viewed visually, it resembles a white dot. If you look at nits under a microscope, you can see that this is a kind of purse in which the larvae develops.
A few days later a young insect, a nymph, emerges from the nits. It resembles an adult, but is slightly smaller in size and its body has a more white chitinous cover.As soon as 3 molts of this cover pass, the nymph becomes an adult and begins to actively feed on blood and reproduce.
Incubation period nits
Nits are the head louse eggs, which are attached at the root of the hair with a special adhesive substance. It envelops a cocoon at birth. Due to this, it is almost impossible to remove them mechanically from the first time.
In nits, the incubation period lasts about 8 days. A large role in the development has a temperature, and the ability to eat the necessary amount of blood. If in winter or at temperatures below +18 degrees the development of nits slows down and even stops, then in the summer period the larvae grow very quickly.
After the start of infection, there may be more than a hundred of the scalp.
How long do they turn into adults?
 It takes 2 weeks to turn into an adult insect. Initially, the nit turns into a nymph. This insect is small in size and cannot reproduce due to an inferior reproductive system.
It takes 2 weeks to turn into an adult insect. Initially, the nit turns into a nymph. This insect is small in size and cannot reproduce due to an inferior reproductive system.
As it matures, it goes through two more stages of molting and turns into an adult insect. They are called imago. Blood is required for their development and reproduction. They are fed several times a day.
Thanks to human blood, they can multiply and multiply. It takes 45 days to grow an entire population of hair. A person experiences persistent itching that occurs due to multiple lice bites, which can be several dozen.
The life cycle of ectoparasites
Lice do not fly or jump. Therefore, lice infection occurs due to contact with the patient or through his personal belongings. Enough to get to the hairy part of the human body, as the parasites begin to immediately feed on blood. An adult insect without human blood can live for one day, so it is very important for them to constantly receive food.
Having got on the person at females, pairing with the male occurs. Within a few days, she lays about 4 eggs. With pediculosis, there is no incubation period. Lice feed on blood, mate and lay eggs.
This happens until the end of the life cycle of an adult insect. Lice live for about 2 months and during this period they lay up to 140 eggs. After 2 weeks, another adult appears from the larvae. This can last indefinitely if the patient does not start treatment.
To avoid unpleasant effects, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment when nits are detected. You can use drugs or traditional medicine prescriptions. Men can shave their heads. In this case, there will be no place for nits to be fixed, the development of parasites will stop, and the females will die.
Lice life cycle
Lice belong to insects with incomplete transformation. This means that the life cycle of the development of head lice does not include the stage of the typical larvae, which in other insects usually differ greatly in appearance and feeding method from adults.
The adult female mates during the first day or two after the last larval molt, and after a few hours begins to lay eggs. Since the source of food (man) is always “with lice,” they do not have developmental delays that are characteristic of other parasites due to the hunger strike.
Lice basically do not know how to starve. Each insect should eat every few hours, and in the absence of food for two or three days the louse dies. Pubic louse can starve a maximum of 10 hours.
Lice eggs are attached to hairs at different distances from the hair root. Each egg is put on a sticky cap, due to which it is glued to the hair tightly enough. This design of the egg and cap is called a nit. When viewed with the naked eye, it resembles a simple white dash on a hair, but when examined under a microscope, it is a neat handbag, tightly wrapping its hair.

From the nits, the larva of the first age hatch fairly quickly.It is very similar to an adult insect, but has very small dimensions and an underdeveloped reproductive system. After the first saturation, such a tiny larva immediately sheds and turns into a nymph.
The nymph in zoology is called insect larvae, which differs little from adult individuals (imago). For example, cockroaches and grasshoppers have nymphs. But the butterflies and beetles in the development cycle present a real larva, absolutely no resemblance to the imago.
The rapid cycle of lice development suggests the presence of only three molts and, accordingly, three nymphs ages. Molts are required by nymphs for the reason that the chitinous cover of their body is not elastic and cannot grow along with the soft tissues of the insect. Accordingly, when such a “suit” becomes small, the nymph changes it.
After the third molt, the nymph becomes an adult insect. Female lice every day lays 2-4 eggs - up to 140 in a lifetime.
Body and head lice are quite different from each other in the details of the structure of the legs and some features of the body shape. If placed in a limited amount of lice of different forms, they can even multiply (interbreed), and after several generations the differences between them will disappear.
Reproduction of lice on the head: the process under the microscope
Reproduction of lice in humans is replete with interesting details. For example, the process of hatching larvae from an egg is entertaining - an insect pierces the lid of a nits with its jaws, but cannot get out on its own. But at this time, the larva breathes actively, passing air through its digestive system and pushing it through the anus. The air accumulating in the lower part of the nits pushes the larva out of the cap, and it falls on the scalp, where it starts feeding right away.

Different stages of lice development are characterized by different periods of existence:
- 5-8 days develops nit
- 1-3 days the larva needs to turn into a nymph of the first age
- 5 days develops nymph of the first age
- 8 days nymph develops second age.
The adult louse lives from 30 to 42 days, and the recorded longevity record for these insects was 46 days. The longevity and reproduction period of lice narrowly defined in terms are due to the stability of the conditions in which head lice live at all stages of their development.
Females of lice mate with males in the first hours after leaving the nymph. One copulation is enough for them to fertilize all the eggs in the body. Then every day the female lays several eggs. The head louse has about 2-4 eggs per day, the pubic one has 1-3 eggs, and in the case of clothes louse it is up to 10.
Accordingly, in my life:
- female head lice lays up to 140 eggs (usually about 80)
- female pubic lice leaves about 50 eggs
- female louse lays up to 300 eggs.
The egg itself in the gonads of the female is smeared in a sticky secret, part of which is removed from the oviduct before the egg. This secret forms the shell of the nits, due to which it is attached to the hair.
After laying the eggs, the secret hardens and provides a reliable attachment of the eggs.
The video below clearly demonstrates how lice breed.
Interesting shots: about lice, their reproduction and the life cycle as a whole
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the life cycle of lice takes place on the surface of the head of the same person. However, in the case of close contact of people with each other or when scratching, an insect may fall on the head of another person and give rise to a new population here. This is the transmission of lice.
Conditions under which lice breed
Propagation of head lice occurs in fairly limited temperature ranges. Their nits stop developing at temperatures below 22 ° C and above 45 ° C. The optimal temperature for the rapid course of the life cycle of a head louse is 30-31 ° C.
Head lice breed as quickly as possible with a large number of them on the head, when females and males do not have to search for each other for a long time. These parasites are species-specific, that is, they cannot infect another host besides man and some monkey species very close to him.

It is believed that with the greatest speed lice breed in places where large numbers of people live together. They were a great misfortune in times of war and people living in barracks.
Video: the potential danger of lice and methods of dealing with them
Head lice - parasites are highly specialized not only by the nature of their food, but by the place of their existence. They can dwell only n.
Generally speaking, species of lice are numerous - only in mammals there are more than 500 species of these insects. At the same time on the person parasitize.
Lice are obligate and very highly specialized human parasites. They are absolutely not adapted to life outside his body or to other animals. L
Your phone has been sent.
Soon we will call you back.
thanks for the information
Thanks for the information.
Thank! I learned a lot of new and interesting things!
Everything is very interesting and even a lot of useful information. But one question is in my head: where do they come from right from the beginning? Would love to find out. I have never had lice myself, so I can't imagine what it is like. My daughter's niece had lice, and decided to climb on the sites and find out their origin. Everywhere they write that from another person, and where did they come from? Do not understand. Thank you in advance.
Just on a clean head lice soon and go (((
Taken from the dirt. Often parents don’t look after their children, especially parents whipping, and here’s the result.
At the moment it is rather the trouble of wealthy families. Children at school lend each other things, change, unaware of the danger. My girls picked up this stuff 3 times. 1 time at school, the boy in the next classroom for about a year went lousy, simply because his mother had poor eyesight and she could not process it normally. Although I could elementary shave him nakedly, but no, I myself suffer, the child suffers, and let everyone else suffer. The nurse from the school told me about this in confidence, I was shocked, I need to fire such doctors. As a result, the boy was sent for processing to the KVD. The second time we picked up at the same school, also a boy, but the other one came from sports camps from Italy. Believe me, my parents can not afford this.
I again with shampoos, comb, with an iron throughout the apartment, even stroked plush toys and carpets. By the way, the hair of my beauties is lower than the priests, i.e. meter length. Now I am again with irons and shampoos ... I went to the water park a couple of times (by the way, also not cheap) - and this is the result ... You can also pick up in the store, measuring things that the infected person measured to you, sitting in the cinema on upholstered chairs, headrests every time no one disinfects, in the school in the locker rooms, in physical education classes (children tumble on the mats, that's enough). The list is endless. The main thing in this business - time to see and take action. It’s good that I’m on vacation now and I have the strength, and so I would hang myself ... I had a thought to cut their heads off ((
Tell me, why do we need an iron?
What nonsense? Dirty all.
I measured the cap in the store, in the end the whole family became infected. For the first time infected in Indonesia in the pool. They live quietly in the water, so water parks, swimming pools and saunas are places of heightened danger.
Lice: Parasite Features
The human louse is an ectoparasite known for a long time. A small insect (4–5 mm) is parasitic only in humans. The area is associated with the insect species:
- the head louse is located inside the head of hair,
- pubic "trades" in the genital area, under the arms, on the eyebrows, eyelashes,
- wardrobe is covered in folds, the seams of underwear, bed linen.
With the naked eye to notice a louse is difficult. It has an unremarkable appearance: color, “merging” with the color of human hair (range from gray to brown). Unpleasant manifestations, the result of vital activity, are felt some time after infection: a kind of incubation period has an effect.
Bloodsucker is perfectly adapted to dwell in its environment. Clenched legs with claws provide a secure attachment to the head of hair. Subtle scent provides the perfect orientation. A powerful piercing-sucking mouth with needles for breaking the integrity of the skin, a proboscis pump that draws blood in, provides the nourishment process.
The first signals about the appearance of parasites are noticeable with a special sensitivity of the organism already for 3–7 days in the form of increasing itching. In the same period, found "dandruff", which can not be shaken off (nits). When lice hatch from eggs, the symptoms increase. The timing of detection depends on how quickly the parasites get divorced. How to understand that you have lice, signs of pediculosis, read on our website.
Breeding principle
Getting to the new owner, lice continue to live. First of all, it is nutrition, reproduction. To saturate, an adult individual uses human blood every 4 hours, and a nymph released from an egg - at least once every 2 hours.
The amount of blood consumed is small, the bite is painless, but the parasite's saliva contains a toxin that provokes allergic irritation. Most often in a mild form: in the form of itching. The greater the number of bites, the more pronounced the symptoms become. What the lice bites look like can be found on our website.
An important point! The increase in the number of feeding individuals directly depends on the rate of reproduction of the parasites. Once in the new environment, the female continues the breeding cycle: laying eggs. Every day, 1 individual holds up to 4 cocoons. During the full life cycle (about 45 days), the female produces about 150 eggs.
Nits phase
 As a result of mating adults, all the eggs that the female has are inseminated. A single fertilization starts the breeding process the length of the insect's life. therefore hitting even a single female into a new territory will provide a quick increase in numbers.
As a result of mating adults, all the eggs that the female has are inseminated. A single fertilization starts the breeding process the length of the insect's life. therefore hitting even a single female into a new territory will provide a quick increase in numbers.
The first laying of eggs occurs within a few hours after insemination by the male. The female is located on the hair near the root. From the genitals releases sticky mucus, followed by an egg.
Viscous mass envelops the fruit, forming a kind of cocoon. The mucus quickly hardens in air, providing a reliable fixation, protection.
The resulting education is called nits. This substance can not be washed off with shampoo, it is difficult to comb out with a comb. The shell of the nits is reliable protection, even insecticides do not penetrate inside. After the larva leaves the dry nits, it remains attached to the hair.
The nits phase lasts about 8 days. At this time, the formation of the organism of the insect. The ripened larva gnaws the cocoon shell in search of food. A larva (nymph) that has come out is hungry. In order to satisfy the need for food, to stimulate growth, an individual proceeds to an enhanced diet.
The duration of the development of lice in nits depends on the environment. Under ideal conditions (air temperature is +31, moderate humidity), the larva is able to leave the cocoon for 1 day. With a sharp deterioration in the situation (decrease in temperature to +10 degrees) will result in a slowdown in development, which will be approximately 10 days.
Complete loss of nits occurs only under very harsh conditions. With a long stay of the carrier in the frost at 20 degrees (from 2 hours) the larva dies inside the egg. Adult nymphs are able to die at -10 degrees. Less pronounced freezing temperatures cause the embryo to suspend development.This is due to the fact that at the base of the skin, where nits are attached, it is always warmer due to the natural heating of the living human body.
High plus marks of air temperature also affect the development of the insect. At +40 degrees adults stop reproduction, feeding. In the temperature range of 40–50 degrees of heat, the insects perish. Nits lose their vitality at a temperature of 50-60 degrees Celsius.
Larva transformations
 The nymph, unlike a fully formed individual, has a smaller body size, is not capable of reproduction. The appearance of the larvae, the way of feeding is similar to adult representatives. Such a strategy is called incomplete transformation.
The nymph, unlike a fully formed individual, has a smaller body size, is not capable of reproduction. The appearance of the larvae, the way of feeding is similar to adult representatives. Such a strategy is called incomplete transformation.
Gradually the body of the larva grows, and the protective chitinous shell remains the same (approximately 3 days after leaving the cocoon). To adjust the mismatch you have to reset the hard shell. The body of the naked nymph under the influence of air hardens. The grown larva gains a former look, differing only in the changed dimensions.
The molting nymph (1st generation) continues its previous activity for 2 days. Then, re-shedding occurs. Appears nymph 2nd generation. This creature prepares for adulthood for 3 days (laying of the genitals takes place).
The last molt turns an insect into an adult louse (imago). Mature parasites start mating, launching a new development cycle.
Under favorable conditions, the complete cycle of the formation of life from an egg to an adult individual takes 15–16 days. Lack of adequate nutrition, deterioration of temperature conditions lead to the extension of developmental stages up to 20-30 days.
Adult
An insect that has become an adult finds a partner for 2 days, mates. A day after fertilization, the female begins to lay eggs. Daily 2-4 pieces. Louse secures eggs at the roots of hair. The location of the nits indicates the laying period.
For 30–40 days of existence, each imago produces 120–160 eggs. How many nits will be formed depends on the living conditions of the insect. Given this reproduction rate, it becomes clear why lice begin to spread so quickly.
Parasitic activity, supported by comfortable conditions of stay, does not allow lice to lose food. Bloodsucker constantly has a power source. The parasite is devoid of enemies: no forces are spent on survival. A female enough to mate 1 time to reproduce offspring for life. These factors determine the ideal conditions for population growth.
Interesting fact. An adult male has a short life. After going through the developmental phase to the mature insect, the male mating parasitizes for about 7 days. Then, the death of the insect comes.
The main methods of infection
 Distribution of lice occurs exclusively by contact. Parasites crawl from one hair to another, continuing the development cycle in a new place. This may occur by chance with close contact with the carrier.
Distribution of lice occurs exclusively by contact. Parasites crawl from one hair to another, continuing the development cycle in a new place. This may occur by chance with close contact with the carrier.
If the host conditions deteriorate, the parasite itself seeks to find a more suitable environment. Therefore, at the first opportunity to "catch" on other people's hair, it does this.
The greatest danger to infection is close crowds of people:
- gathering of disadvantaged citizens
- public transport,
- public places with human masses.
Close attention is paid to children. They, by virtue of the behavioral pattern, are most susceptible to infection by parasites. This is due to their spontaneity, a tendency to close contacts in games, neglect of hygiene.
Understanding how quickly head lice multiply is important in order to be aware of the scale of a disaster during an infection. Timely diagnosis, prompt action taken, will help to quickly deal with the problem.
Useful videos
Lice. Causes and treatment.
Head lice.How to get rid of uninvited guests?
Development of pediculosis
A person becomes infected with parasites through close contact with the patient, his things. At first, the insect doesn’t give out in any way, because the itch from lice bites appears after a while.
Irritation of the skin is not caused by the bite itself, but by the parasite's saliva. In order for an allergic reaction to occur, a certain amount of allergen must accumulate. This usually occurs within 5 days.
The first thing a female does on a man’s head is to lay eggs. The life cycle of the development of head lice and nits is 16 days. After exiting the egg, the larvae immediately begin to parasitize. They are fed every 2 hours. Itching begins, pediculosis becomes pronounced. Adult female eats every 4 hours. To get enough, she has enough minimum amount of blood. Nutrition is necessary to replenish vitality, reproduction of offspring.

Reproduce after infection rapidly. Daily the female lays about 4 eggs. The incubation period does not differ in duration, so within 1 month a large population of parasites appears on the human head. The patient becomes pediculosis peddler, his whole life turns into a nightmare. Lice are transmitted during the embrace, close contact with the head of another person.
Egg cycle
Lice refers to insects with incomplete transformation. In her life, there is no larval stage, which is distinguished by its appearance and feeding habits.
Patients are always interested in the question of how many eggs one louse lays, since infection occurs very quickly. An adult individual begins to produce offspring several hours after mating. Daily appears from 2 to 4 eggs.
Lice breeding is a fun process. Male seminal fluid fertilizes all the eggs of the female. One mating is enough for the female to lay its eggs all its short life. The female no longer needs a partner to continuously produce offspring - which is why females lay so many eggs.
Lice attach eggs - nits at the base of the roots of the hair. At a distance of 1 cm by the location of the nits in the thread you can determine how long the eggs were laid. Initially, sticky mucus comes out of the genitals of the louse, followed by an egg. The substance hardens, provides reliable fixation nits. It can not be removed when combing the usual comb, rinse with shampoo and other hair care products, which strongly distinguishes nits from dandruff.

The shell of the nits is so dense that it does not miss any insecticide. The larva develops safely after a “heavy attack”. The only method of dealing with the larvae in the shell - combing nits. For these purposes, use a comb with fine pitch or a special comb from the lice.
The rapid stage of development of the larvae
In an egg, an insect develops about 8 days. Formed individual gnaws the shell, but can not get out. Begins to actively breathe air, release through the rear opening. At the bottom of the egg carbon dioxide accumulates, which pushes the larva out. Lice appear a new generation - nymphs.
The larva in appearance is no different from imago. Gives her the recent appearance of the light body size.
It is no less curious how quickly the head lice multiply. Immediately after leaving the egg, the larva begins feeding. Every day the body grows in size. Chitin shell remains unchanged. To get rid of him, the nymph just drops it. After a few hours, the upper shell of the body hardens. The young individual again takes on its former appearance, but is distinguished by its large size.
Total larva passes 3 molts. Development with transformation lasts 8 days. At the last stage, the nymph forms genitals. The insect turns into an adult - imago. New parasites immediately begin to mate.
Stage of development of lice:
- nit - about 8 days,
- larva before molting - 3 days,
- 1st generation nymph - 2 days,
- 2nd generation nymph - 3 days.
Terms of development and reproduction of lice depend on the availability of power source, temperature. Under adverse conditions, the process is extended to 20-30 days.
Adult lice life
Imago lives 30-42 days. For all his life lays about 140 eggs. The short lifespan of lice is due to the constant availability of food, comfortable temperature conditions.

Lice never go hungry, the opportunity to drink blood is always there. Do not waste time searching for a partner. One pairing is enough to reproduce offspring for life. Comfortable temperature for existence and development is within 31 ° C. On the head of a person the range is always maintained at any time of the year.
The reproduction period of the louse is adjusted if the louse crawls on the head of another person or is on a pillow or headgear for some time. Outside the human head, the insect can live for 3 days.
Head louse is not able to parasitize on other parts of the body, infect animals. Pediculosis transmits only lousy people, his hats, combs. The development of lice and nits occurs unnoticed by humans. Gives out their existence on the head constant itching, which increases in the evening. To breed, to give offspring is capable of a strong male who dies a week after mating.
In ancient times, the appearance of lice was considered an infection. It was assumed that the parasites developed for a long time under the skin, and when exposed to favorable factors, they crawled out. This explains the rapid reproduction of lice.
Other human lice
In addition to the head louse there is a wardrobe or clothing, pubic. The latter was called ploschitsa.

- Pubic louse is different from the head appearance - more like a small crab. Parasitic pubic. With a strong infection, the plower is found in the armpits, on the eyebrows, on the eyelashes. The hair on the head does not fit the structure. Infection occurs during sex, through contact with towels, personal items. Parasites multiply rapidly. During the day, the female lays about 7 eggs. Pubic pediculosis manifests itself within 2 weeks.
- A clothes louse is almost the same as a head louse. Repeats the entire life cycle, especially reproduction. The only difference is the habitat - a person's personal belongings, bedding. Parasitic on the body, except the pubis, head. Without food can live for about 5 days.

How lice multiply, has been known for a long time. It’s well understood where the parasites come from. all ways of infection. You can get rid of lice for 1-2 procedures. Pediculicidal drugs can be bought at the pharmacy or use folk remedies. At risk are children, dysfunctional families, people without a certain place of residence. If left untreated, infection in the wounds of the bites, complications develop.
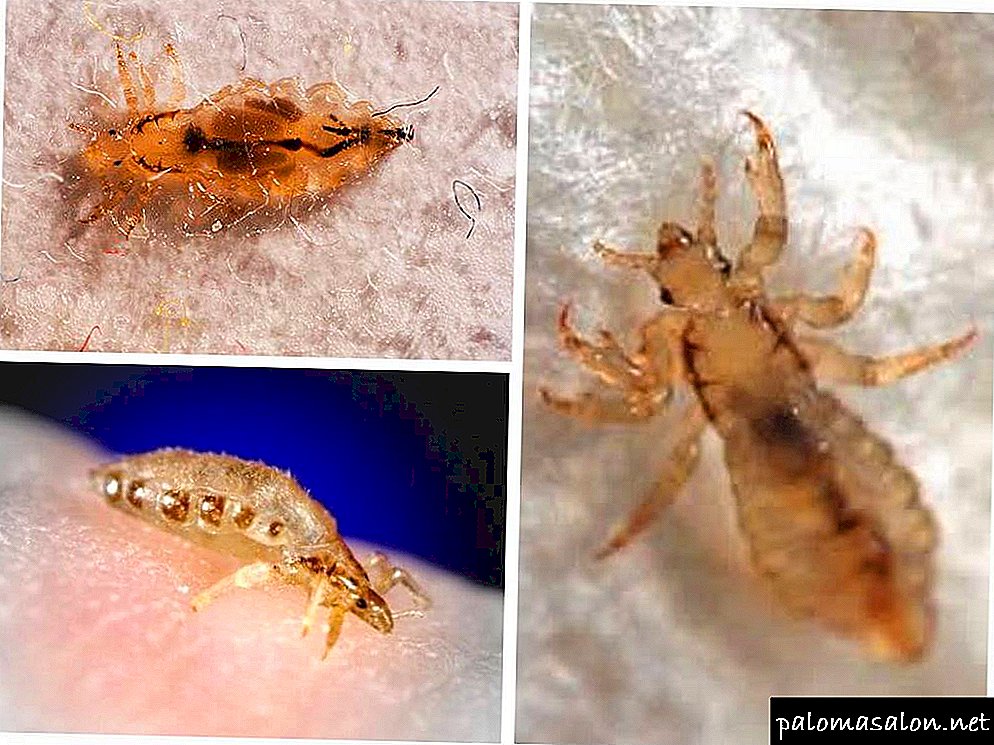
What are lice
Before answering the question of how quickly the lice on the head multiply, let's see what these little bloodsuckers are. Head lice are parasites that feed exclusively on human blood. Their natural color is gray, but they, like chameleons, can adapt to any hair color.
All their not very long life (about 4-5 weeks) lice spend on human hair. If in some random way the parasite is outside its habitat, then this means for it a painful death within 2-3 days.
The length of the female parasite is about 4 mm, and the male is slightly less - 2-3 mm. Louse has three pairs of legs. And at the end of each of them there are peculiar hooks, with the help of which they are firmly attached to the core part of the hair. Parasites move very quickly, for example, they can cover a distance of 12 cm in just half a minute.
Lice species
How fast do lice breed? Let's look at some of their views:
- Clothes (so-called wearable). They carry out their livelihoods exclusively in places such as beds, sofas and clothing.
- Head. They chose the scalp of a human head (beard, mustache and hair).
Important! Head louse is less dangerous for mankind compared to the closure, as it is not a carrier of such a terrible disease as typhus.
- Pubic (or ploshitsy). They live on the external genitals and cause itching and burning in this place.
On a note! Each parasite species has its own life cycle. But head lice reproduce most slowly, and pubic insects are fastest.
Parasitic insects that inhabit our smaller brothers
Can lice living in the hair of domestic animals (dogs and cats) - lashes, multiply in humans? No way. Sometimes these insects can randomly switch to the human skin, but they will not linger there for long. This is not their territory. By the way, head lice (or other varieties) from people also can not go to our smaller brothers.
Important! Voyoedy lay nits in animal fur and in their habitats (for example, on bedding or in booths). To feed, insects jump on animals. In the event that a dog or a cat is absent nearby, they begin to bite a person’s feet, since it doesn’t matter what kind of warm-blooded body they have for lunch today.
How and where can I get infected?
Before answering the question of how quickly lice multiply after infection, let's look at how these parasites can be in your hair.
Infections with pediculosis can be anywhere. It can be beauty salons or hairdressing, if they neglect to disinfect the instruments used.
Or in public places such as kindergartens, nurseries, schools, summer camps, motels, shopping malls or sports clubs.
It is very easy to become infected with pediculosis: the parasites simply jump from a sick person to a healthy person and begin to multiply rapidly. Infection can also occur when using other people's personal hygiene items, such as a pillow, comb, towel, clothing, hat, etc.

Symptoms of Pediculosis
It is worth thinking about how quickly lice multiply. To do this, consider the signs of pediculosis:
- Constant burning and severe itching of the skin of the head, namely behind the ears, as well as in the neck and neck area.
- The presence of scratches and bites in the temples and neck, as a result of which red dots are formed.
Important! Itching, which leads to irritation and wounds (as a result of scratching), increases the risk that the infection can easily penetrate the damaged areas of the skin of the head.

- With a thorough examination of the scalp, the direct presence of insects can be observed.
- The presence of a large amount of dandruff.
- The hair looks rather dull and sticky.
- Temperature rise.
- Sometimes there is some hair loss.
- Decreased appetite.
- There is a general deterioration in the health of an infected person, including depressed mood.
- The presence of inflamed lymph nodes.
Parasite incubation period
Consider what happens at the early stage of head lice. That is, when a person is just infected. What is the incubation period? This is a hidden course of the disease, when the symptoms are still not sharply manifested. Obvious signs of the disease will be in about 16-20 days, during which, besides you, all family members and people who are close to you will become ill.
How fast does a person's lice reproduce? The main stages of the transformation of larvae in adult insects:
- An adult individual lays eggs (nits) on human hair, at a distance of 1-3 cm from the root, using a very strong adhesive substance (it is produced by the glands of the female) that cannot be washed off with either shampoo or water.
On a note! The number of eggs laid by the female parasite during the month (this is how much she lives) can reach several hundred.

- The larvae hatching from eggs after 8-10 days undergo a process of moulting and become nymphs (that is, young individuals not matured in the sexual plan).
During this period, a sick person can already infect others.
- After two molts (approximately 7-10 days), the larvae are already transformed into adult parasites, namely, adults, which have reached puberty and are able to reproduce.
After the appearance of new individuals, the disease is no longer impossible to notice. Insects begin to actively secrete very unpleasant enzymes and it is rather painful to bite.
What determines the speed of the incubation period
How quickly do lice on the head of a child or an adult multiply? It all depends on the temperature conditions at which the reproduction of parasites occurs:
- At a temperature of about 37 degrees nits, it develops in 5-8 days, and at 23 degrees, this process will take about 2 weeks.
- If an infected person spends most of his time indoors, the temperature of which is below 22 degrees or above 40, then insect reproduction is impossible.
If the temperature varies from 10 to 20 degrees, then the parasites can hold out for 10 days without food.
Disease treatment with drugs
Regardless of how quickly lice in a child multiply, at the first sign of a disease, you should immediately seek help from a medical institution. The doctor will schedule an examination and, based on the results, write out the necessary medication. Moreover, today doctors have a huge amount of anti-pediculosis drugs, with which you can cope with the disease at an early stage.
You already know how fast the lice on the head multiply after infection, but remember - only a doctor can confirm that you have parasites or their absence. Uncontrolled intake of anti-pediculosis drugs (and in some cases unjustified) can lead to serious complications, because almost all drugs for lice have side effects.
Prevention
Based on how quickly the lice multiply, we recommend that preventive measures be taken to help prevent or quickly remove the nidus of the disease. This especially applies to the moment when your child returns from rest. It would be appropriate to conduct a very thorough examination of the scalp on the head (to be more precise, the area behind the ears, back of the head and temples) of your offspring.

Remember that the louse is quite similar to dandruff, only it is difficult to shake off the hair. If you manage to abstract from a feeling of disgust, then you can remove the alleged nits and crush them with ruthless nails. If at the same time you hear a characteristic crash, then the disappointing diagnosis is confirmed - your child has lice.
Based on how quickly the lice multiply, they must be destroyed immediately after detection, not only on the head of the parasite's carrier, but also on all members of the family or team in which you work. Otherwise, the efforts will be in vain. Do not be ill!
Reproduction rate
How quickly do lice grow on the head? Lice multiply by laying white eggs (nits), which are firmly attached to human hair at the very roots with a sticky mass.
Terms, or rather the reproduction period of lice in humans depends on the ambient temperature. So, producing about four eggs a day at an optimum temperature (25-30 degrees), the female can stop laying them when the temperature drops below 12 degrees.
Later on, larvae appear from the eggs. Speed, development and reproduction of lice, i.e. The transformation of the larvae into a nymph of the first age depends on the ambient temperature.So, at a temperature of 30 degrees, the transformation will occur in a day, and at a temperature of 10 degrees it will take ten days.
The stage of the nymph of the first age lasts five days, eight more days are allotted to the stage of the second age of the nymph and, finally, the insect reaches the stage of imago (adult insect).
Before turning into an adult insect nymph to shed three times. This is because the shell is not keeping up with the growth of the body, torn, and the nymph just throws it off. Lice can live not only in the hair, but also on the eyebrows and eyelashes of a person.
How lice look different sexes
Lice are heterosexual parasites. Female and male individuals differ in size, appearance, structure of some organs.

The human body is inhabited by the pubic, ward and head forms of the parasite. Lice that live on dogs and cats in humans don't take root.
Fertilization
In humans, lice reproduce in the same way as all heterosexual insects - after mating, fertilization of the female eggs, maturation and laying of eggs occur.

Features mating lice:
- female individuals are ready for fertilization and laying eggs immediately after the end of the larval stage of development,
- the duration of the fertilization process - 20–70 minutes, the seminal fluid is stored in the female’s abdomen, consumed throughout the parasite’s life,
- eggs are formed and fertilized as you move to exit from the oviduct, while moving the eggs are covered with a dense protective shell,
- After the mating process is completed, it takes several hours to fully mature nits.
Egg laying

For many years I have been studying intestinal problems, in particular salmonellosis. It is terrible when people do not know the true cause of their diseases. It turns out that the whole thing in the bacteria Helicobacter Pylori.
These bacteria are able to live and reproduce not only in the intestine, but also in the stomach. Being introduced deep into its walls, the larvae are distributed through the whole body by the blood flow, getting into the heart, liver, and even into the brain.
Today we will talk about the Notoxin natural product, which turned out to be incredibly effective in treating salmonellosis, as well as participating in the federal program “Healthy Nation”, thanks to which the product can get for FREE when applying until November 27th.
After completion of the fertilization process, the female begins to move actively in search of a better place for laying eggs.
How do lice develop?
Lice are insects with an incomplete development cycle; they do not turn into larvae, which differ significantly in appearance and in the way they absorb food from adults. In any species of human parasites, a nymph hatching from an egg, which then turns into an imago.

For how many days does an egg transform into an adult insect:
- Egg - the initial stage of development of parasites. Depending on the type of insect and the temperature values of the environment, it continues from 5–20 days. Lice like heat, so they multiply the fastest in the summer, with a decrease in thermometer performance up to 22 degrees and below, all processes slow down. Nn is an egg covered with a sheath of sticky substance.
- A larva appears from the egg, but it cannot get out of the cover on its own, so it begins to breathe intensively. At the same time, carbon dioxide accumulates in the back of the shell, which pushes the larva out.
- Nymph - larval stage of development. Before turning into an adult insect, it molts three times, since the chitinous shell cannot grow in size, as the insect grows, it simply drops it. The gap between the molts is 3-5 days. It differs from an adult individual only by its smaller size, after the last molt through 24–48 hours The louse is ready for fertilization, and after a few hours the young female lays her eggs.
- The imago is a mature individual, the reproductive stage of development, lasts 30–42 daysDuring this period, the female lays new eggs every day.

The full cycle of development from egg to adult under optimal conditions is 15–20 days. 6–8 weeks after infection, the number of parasites can increase several dozen times.
Favorable breeding conditions for lice
Pediculosis is a contagious disease. It is transmitted from person to person through close contact, use of common things, clothing. The disease is more often diagnosed in preschool children.
About the most common skin parasitic infections in the School of Dr. Komarovsky:
Lice love to live more on clean hair, because it is more difficult to pierce the scalp through a layer of fat and dirt, so it is more difficult for parasites to get their food. The optimum temperature for rapid growth and reproduction is 30–32 degrees.
The process of the appearance of lice from nits in the video:
Lice do not tolerate:
- Temperature rise above 45 degrees: if a person's illness is accompanied by intense fever, the parasites move closer to the ends of the hair.
- Low temperatures - the development process slows down as the indices decrease to 22 degrees, and at minus values the parasites die within a few days.
- Lack of oxygen - Some anti-pediculosis products contain silicone. The substance does not kill the parasites, but clogs all breathing holes, which leads to the rapid death of insects.
- Lack of food - parasites feed exclusively on blood. Food required lice every 2-4 hours. Body lice can go a little longer without food, and pubic ones die after 10 hours of hunger strike.
- No hair - parasite paws are not adapted to fasten on smooth skin, therefore, shaving remains the most effective and safe method of dealing with head lice.
- Sharp, strong odors.
Lice outside the human body can remain viable for up to 3 days, feel comfortable in warm standing water, so infection with head lice sometimes occurs after bathing in fresh water with standing water.
Lice differ fertility, multiply rapidly on the human body, feed on blood. The entire life cycle from the larva to the adult individual passes on the body of one host. Infection with pediculosis most often occurs in areas of large concentrations of people. The disease is diagnosed in representatives of various social strata.



